Skin Discoloration: What’s Harmless And When To See A Doctor
This post was last updated on February 4th, 2025
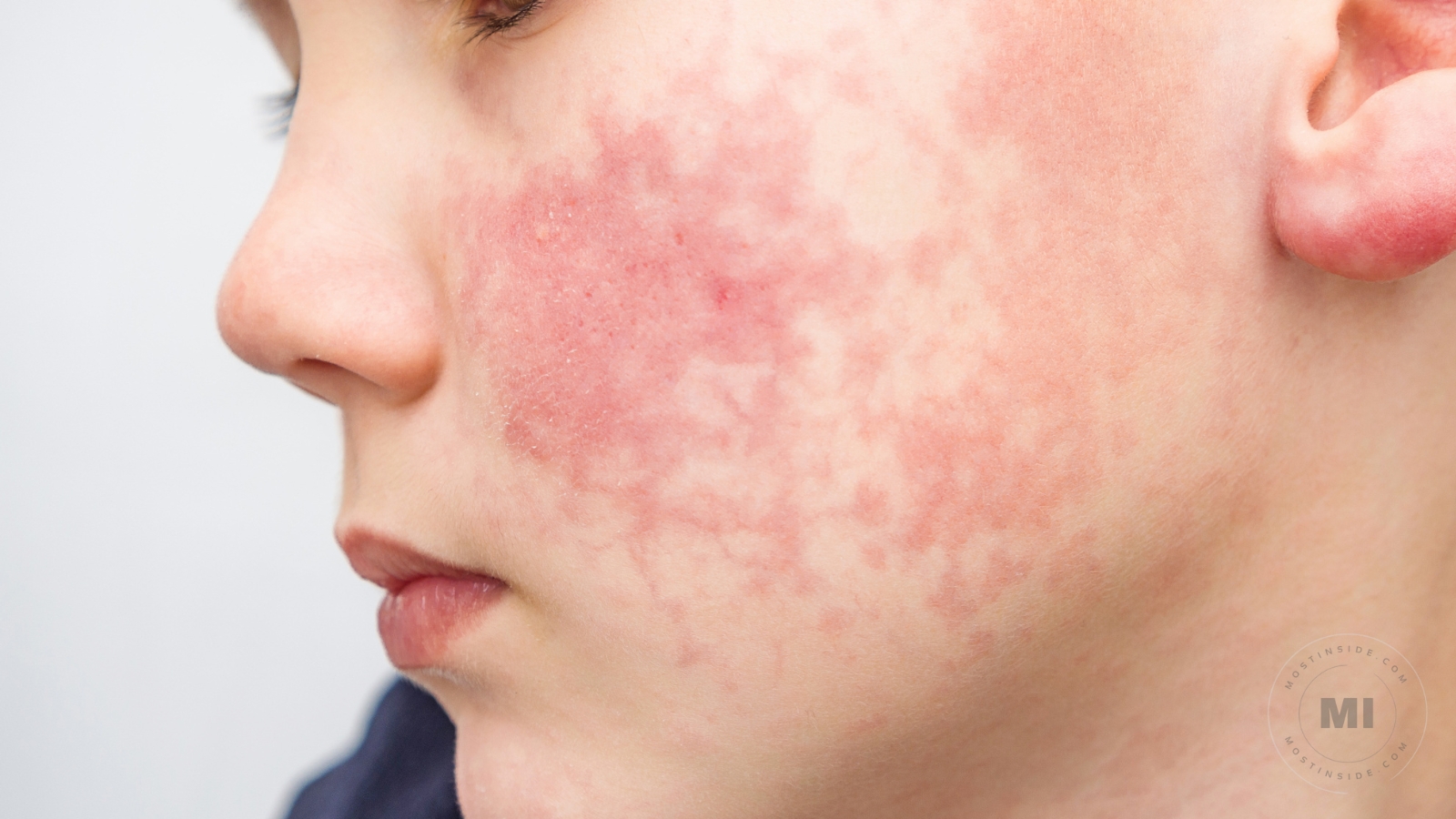
When it comes to the skin, one of the most common concerns is discoloration. For many people, changes in their skin color are harmless and only a cosmetic worry.
However, sometimes worrying spots can appear out of nowhere or even older discolorations can become darker suddenly, leaving you feeling unsure and concerned about what’s going on underneath your epidermis.
This blog post will explore some types of skin discoloration that are generally harmless and others that could indicate more serious underlying health problems.
Causes Of Skin Discoloration
Discolored skin patches, medically known as hyperpigmentation, are widespread and can have various causes. Skin discoloration can vary greatly, ranging from barely noticeable to very obvious.
In most cases, skin discoloration is harmless, but in some instances, it can signal a more serious medical problem. You can get more information on sites like leavittwomenshealthcare.com. Now, you must understand the different causes of skin discoloration to determine when it’s appropriate to seek medical attention.
Birthmarks
Birthmarks are common skin conditions that can affect people of all ages. Various factors, including genetics, trauma, and sun exposure, can cause them. They’re usually benign but can be cosmetically unappealing and sometimes cause psychological distress.
Birthmarks can either be pigmented or vascular. Vascular birthmarks are generally red and result from abnormal blood vessels in the skin. The most common vascular birthmarks are:
Strawberry nevus: This type of birthmark is caused by an overgrowth of blood vessels and capillaries in the skin, resulting in a pink or red discoloration. The cause of this discoloration is still largely unknown, but it’s believed to be due to genetics and environmental factors.
Salmon patches: These are characterized by a pinkish-red discoloration on the face, neck, shoulders, or back.
Port wine stain: It’s caused by an overgrowth of blood vessels in the skin. Port wine stains are usually pink or red and can appear anywhere on the body. They may be flat or raised, ranging from very small to large.
Pigmented birthmarks are usually blue, white, grey, or brown and result from a melanin-related problem. Pigmented birthmarks include:
Skin Pigmentation Disorders
Skin discoloration can occur due to various causes, but one common reason is skin pigmentation disorders. These disorders cause imbalances in the skin’s coloration and ability to produce melanin. Some common pigmentation disorders include:
Vitiligo: A condition where patches of skin lose their normal pigment
Melasma: A condition that causes brown or grayish patches, usually on the face.
Albinism: A genetic disorder characterized by a lack of melanin production, causing light or white skin and hair.
Although these disorders are initially disconcerting, proper diagnosis and treatment from a dermatologist help reduce their appearance significantly over time. Additionally, protection from sunlight offers further long-term defense for those affected by pigmentation disorders.
Skin Infections
Skin infections are common causes of discoloration and can range in severity. Bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites cause skin infections. Some common skin infections include:
Tinea versicolor: This fungal infection affects the top layer of the skin, causing patches of discolored or lighter-colored skin to appear on the body.
Ringworm: Ringworm is caused by a fungus and can cause red or brown patches on the skin. It can also cause itching and flaking of the skin and blisters or bumps.
Candidiasis of the skin. Candidiasis of the skin is a common infection that can cause discoloration in the form of red or white patches. It’s caused by an overgrowth of yeast-like fungus and can be treated with antifungal medications.
Treatment for skin infections typically involves antibiotics or antifungal medications. Seek immediate medical care if you suspect you have a skin infection to prevent its spread and receive appropriate treatment.
Skin Cancers
Skin cancer causes the skin cells to become malignant and grow out of control. Although skin cancer is rare, when it occurs, it can cause skin discoloration. Common skin cancers include:
Basal cell carcinoma: This is a common type of skin cancer characterized by small, red, and pale skin growths or sores.
Squamous cell carcinoma: It’s a type of skin cancer that often appears as a scaly, red, or crusted bump on the skin.
Melanoma: Melanoma is a skin cancer that starts in the cells that produce pigments. It often appears as a dark, irregularly shaped mole on the skin.
Symptoms to look out for include a giant brown bump, a non-healing sore, and rashes that don’t seem like typical acne. It’s critical to be aware of these signs and seek medical attention if you notice changes in your skin’s color or texture.
Skin Rashes
Skin rashes are amongst the most common causes of skin discoloration. Symptoms of skin rashes vary from itchy red bumps on specific areas of the skin, to patches of dry and scaly skin, depending on the type of rash. Some common causes of skin rashes include:
Allergic reactions: Rashes can be a symptom of an allergic reaction to substances such as food, medicines, or chemicals.
Infections: Infections can be caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal infections that can cause skin rashes.
Eczema: A condition that causes dry, itchy, and scaly skin
Rashes may result from an infection or a disease and often require medical attention to assess the severity and receive proper treatment. Knowing the potential causes and the signs and symptoms of skin rashes is vital for everyone to get an appropriate diagnosis immediately.
Sunburn
One of the most common causes of skin discoloration is sunburn. Sunburn happens when the skin is exposed to too much ultraviolet radiation from the sun, resulting in damage to the cells and pigment production. This can lead to dark patches on the skin or even hyperpigmentation, which can be challenging to treat. Sunburn can also cause long-term damage to the skin, making it more prone to wrinkles and age spots.
When To See A Doctor
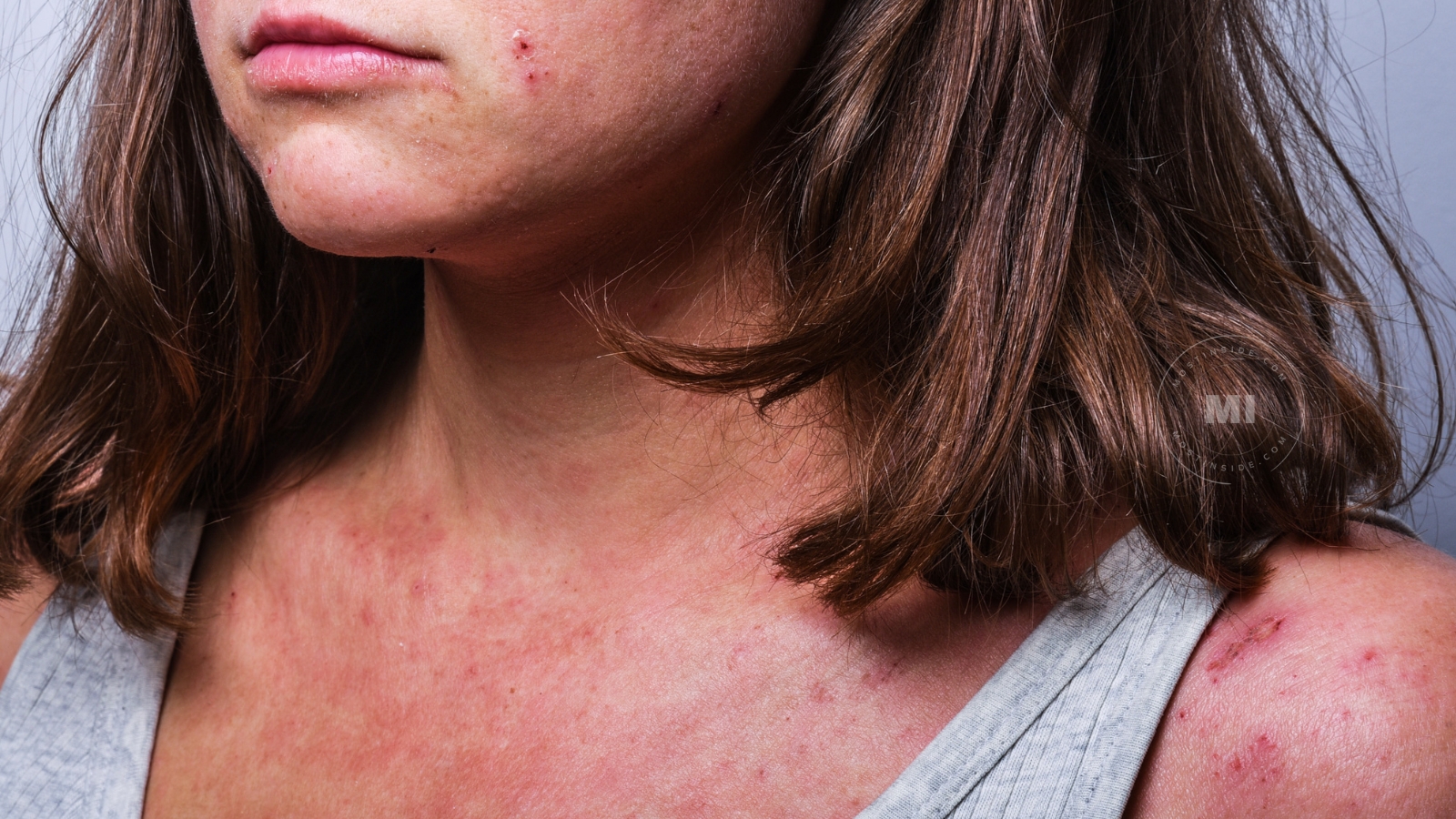
If a new patch of discolored skin suddenly appears and doesn’t disappear, the best thing would be to see a doctor. Get proper treatment, particularly if:
- The discoloration is accompanied by itching, pain, or swelling.
- It’s suddenly or rapidly spreading.
- It covers a large area of skin.
- It’s associated with a rash or lesion.
- There’s a family history of skin disorders.
- It’s not related to a known cause like sun exposure or friction.
The doctor will want to know of any pre-existing medical conditions, when and how quickly the discolored skin patch appeared, if the skin discoloration has changed since it first appeared, and any other related signs and symptoms.
The doctor will then study the affected skin. Depending on his suspicions, he may want to do further tests such as skin biopsy and blood tests. In the case of a skin biopsy, the doctor will take a tiny sample of skin and then study it under a microscope.
Treatment
The treatment plan is dependent on the cause of the skin discoloration. Some common treatments include:
Topical medications: Creams, ointments, or gels can be applied directly to the skin to treat conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and skin infections.
Chemical peels: Chemical peels may be helpful for those with more pronounced discoloration in small areas such as age or sun spots.
Light therapy: Using UV light to treat skin conditions such as psoriasis or eczema
Laser therapy: Using a focused beam of light to treat conditions such as hyperpigmentation or wrinkles
Some people can use makeup to camouflage the affected part of the skin. Still, the best treatment for your skin problem will depend on several factors, including the specific condition, its severity, and your health status. Your health provider can help you determine the best treatment options.
Final Thoughts
Skin discoloration can have many causes, some of which are harmless, while others require medical attention. Benign causes of skin discoloration include changes in skin pigmentation due to aging, hormonal changes, or sun exposure. On the other hand, skin infections, skin cancers, and skin rashes can cause skin discoloration and require medical attention.
If you notice any changes in the color or appearance of your skin, you may need to seek medical advice. A doctor can help determine the cause of your skin discoloration and provide appropriate treatment. Early detection and treatment of skin problems can help prevent more serious complications and improve outcomes.
Recommended For You
Tips to Catch the Useful Diet as Halibut
Most Inside
Most Inside offers high-quality recommendations and valuable updates to enhance all aspects of your life, providing premium guidance and enriching experiences.




