Managing MSD: Effective Strategies for Pain Relief
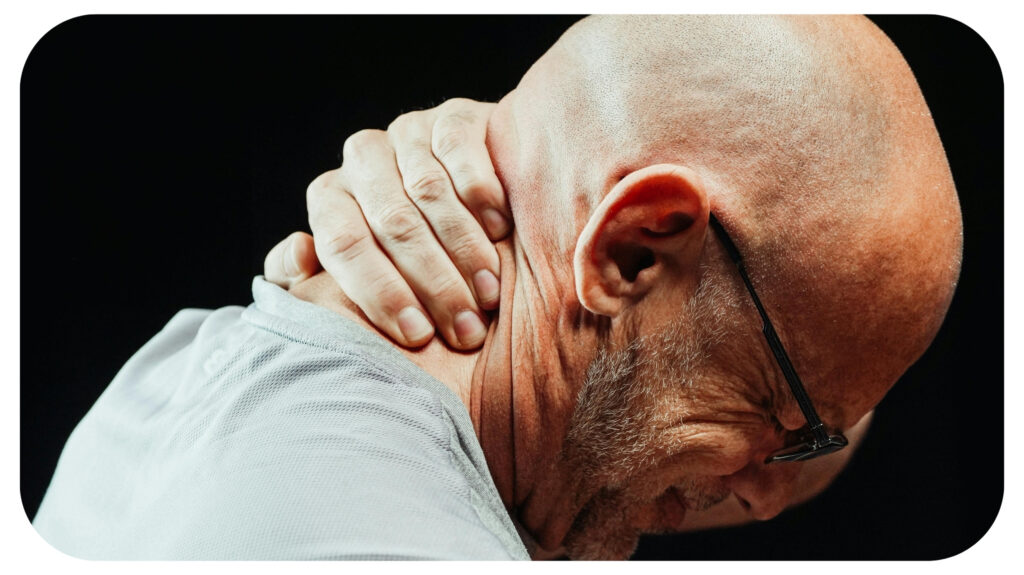
Musculoskeletal diseases (MSDs) are a set of conditions that affect the bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and nerves. Managing MSDs depends on an awareness of these disorders and a choice of sensible painkillers.
This article investigates several approaches and techniques for controlling musculoskeletal pain, therefore providing useful ideas to lower discomfort and improve general well-being.
Understanding Musculoskeletal Disorders
Musculoskeletal diseases (MSDs) are ailments that affect the muscles, bones, tendons, ligaments, and nerves. These issues could be caused by an acute injury, poor ergonomics, or excessive use. Chronic MSDs, such as tendinitis or arthritis, develop over time and severely limit a person’s ability to do regular activities. MSD-related pain produces stiffness, restricted movement, and chronic discomfort.
What is MSD? MSD is a term used to describe a wide range of conditions that impact the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, or ligaments, often leading to pain, stiffness, and mobility issues. MSDs damage not only physical health but also mental and emotional well-being, as the long-term effects of persistent discomfort.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Physical therapy is among the best approaches for controlling MSDs. Targeting activities and treatments meant to increase strength, flexibility, and posture, physical therapy Based on the particular condition of the patient, a physical therapist might create a customized program emphasizing muscle strengthening, joint stability improvement, and pain reduction.
Regular exercise, catered to the degree and kind of MSD, can be quite helpful in controlling pain. By strengthening the muscles around joints, one can lower the strain on tendons and bones and ease the pressure. For pain related to arthritis and other degenerative joint diseases, low-impact activities like swimming or cycling can be especially successful.
Medication for Pain Relief
Pain medications are commonly used to treat MSDs because they provide immediate pain relief. These treatments, which are usually divided into two categories: prescription pharmaceuticals and over the counter (OTC), are used to treat mild to moderate pain and inflammation. OTC options, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and acetaminophen, can be effective.
Although medications can provide temporary relief, their potential side effects must be carefully examined, even if they are beneficial. Pain relievers should be used under the supervision of a healthcare provider and in conjunction with other treatment techniques such as physical therapy or lifestyle modification.
Ergonomic Adjustments
Musculoskeletal pain is sometimes exacerbated by poor posture or improper body mechanics while doing daily activities. Making ergonomic improvements to homes, offices, and even automobiles will assist in significantly reducing the likelihood of MSDs developing or worsening. Simple changes, like adjusting the height of a desk chair, selecting a keyboard that supports a neutral wrist posture, or ensuring that job activities are diversified to minimize extended repetitive motions, can assist in significantly reducing future strain.
Ergonomic treatments aim to reduce unnecessary pressure on the joints and muscles. Maintaining good posture while seated or standing, for example, aids in proper weight distribution throughout the body and reduces strain risk. Taking regular breaks during the day to stand, stretch, or change postures helps to reduce muscular weariness and stiffness, which relieves musculoskeletal discomfort.
Surgical Interventions
When conservative treatment options are ineffective, surgical intervention can be indicated. Surgical therapies for MSDs range from minimally invasive procedures like arthroscopy to more complicated surgeries such as joint replacement or spinal fusion. Surgery is usually considered a last resort when other treatments such as physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes have failed to provide enough pain relief.
The severity of the illness and its impact on daily functioning will determine whether or not surgery is necessary. A joint replacement can benefit someone with advanced osteoarthritis; for example, spinal surgery can be required to relieve nerve pressure for someone with a herniated disc. Before deciding on a surgical course of action, one should always consult with a healthcare practitioner to weigh the advantages and risks.
Conclusion
Effective management of MSDs calls for a multimodal approach combining long-term care, lifestyle modifications, and several therapy techniques. Knowing the underlying reasons for musculoskeletal discomfort and getting quick management would assist in avoiding more problems and enhancing quality of life. Although relieving pain is of first importance, to get long-lasting comfort, one must also concentrate on building the body, correcting posture, and controlling stress. Individuals with MSDs can actively control their disease and reduce discomfort by means of physical therapy, medicine, ergonomic changes, and mental health practices together.
Recommended For You
Types of Plastic Surgery
Most Inside
Most Inside offers high-quality recommendations and valuable updates to enhance all aspects of your life, providing premium guidance and enriching experiences.




